Doctor On-Demand App Development: Tips and Costs
 8 August 2022
8 August 2022Wondering how to develop a doctor on-demand app? Let’s discuss the doctor-on-demand market, app types, monetization strategies, tech-stack, and step-by-step build-process when hiring an on-demand app development company. You’ll receive an estimate of the development costs and an overview of apps revolutionizing the industry.
Doctor on-demand app market
Doctor on-demand entails the provision of virtual healthcare services — pertaining to mental, preventive, urgent, chronic, and primary care — by board-certified practitioners through electronic devices such as computers, tablets, or mobile phones. It falls under the realm of telemedicine services.
Fortune Business Insights™ estimated that the market was worth $144.38 billion in 2020. It has one of the most promising outlooks, with experts predicting a market size of $636.38 billion in 2028.
Contact us now to discuss your Doctor On-Demand app development project!
COVID-19 impact
Telehealth services became increasingly important during the Сovid-19 crisis as a solution for many problems that afflicted the industry.
The pandemic imposed unprecedented economic challenges in the healthcare sector. American hospitals and healthcare systems lost on average $50.7 billion dollars per month as restrictions on movement and fear of infections kept people away from in-person appointments.
As anticipated, virtual telehealth appointments experienced a huge uptake as a substitute for outpatient appointments. An HHS study revealed a 63-fold increase in the utilization of telehealth in Medicare visits from 840,000 in 2019 to 52.7 million. States recording the highest utilization included Massachusetts, Vermont, Rhode Island, New Hampshire, and Connecticut. Adults were more likely to seek telehealth services at 65 visits per 10,000 people compared to 50 visits per 10,000 in children.
Virtual care is here to stay — with 63% of people who had previously used telehealth during the pandemic hoping to use it again in the future.
Popular apps on the market
Some of the most popular doctor on-demand apps on the market include:

Teladoc: Patients can easily access a network of medical specialists and therapists through the online portal or app. Doctors are available 24/7 via audio or video calls. Teladoc acquired Livongo — an app providing support and doctor guidance for chronic diseases — was estimated at $18.5 billion in 2020.

MDLIVE: The app promises fast and hassle-free healthcare from board-certified doctors and licensed therapists. Using the app is quite easy. Patients can create an account and schedule a live doctor visit. The service prioritizes transparent pricing with no surprises, with the website giving a range of how much services may cost.
Amwell: Patients can enjoy 24/7 doctor visits with prescriptions sent straight to their pharmacy. The telemedicine app has recently reported a surge in its telehealth visits to 1.8 million in Q1 of 2022.
Doctor on Demand: Founded in 2013 by Phil McGraw (also known as Dr. Phil), Doctor On Demand offers access to board-certified therapists, psychiatrists, and doctors. It works with all the major health plans, and users can sign up for free and check their coverage. Grand Rounds and Doctor on Demand merged in 2021 to form a multibillion-dollar entity.
Types of doctor-on-demand apps
Before undertaking doctor-on-demand appointment app development, it’s crucial to recognize the app types in the space. This can help with idea development:
- Real-time live conferencing: Apps have live video and voice streaming capabilities, allowing remote doctor and patient interactions. Examples include Doctor On Demand, MDLIVE, and Teladoc.
- Remote patient monitoring: The applications allow doctors, nutritionists, and other medical experts to monitor their patient’s health remotely — for convenience or where in-person monitoring is not feasible. Patients can recover at home and lower costs by reducing time spent at hospitals. Apps can interface and collect data using wearables such as Fitbit. Examples include Diabetes:M and UTM:RPM.
- Store-and-forward telehealth: The apps deal with the asynchronous transmission of medical data (images, symptoms, and other information) from patients to physicians for asynchronous virtual care. They may facilitate the transmission of medical data to other physicians for evaluation. Examples include the MiiSkin skin tracking app.
- Physician-to-physician consultation: Another practical implementation is a physician-to-physician consultation app, where a general doctor can access a specialist’s network. Apps may come with the capability to share medical data quickly.
- Medical imaging: The apps may provide clinics with access to a network of remote radiologists, who can review X-rays, MRI, PET, and other images produced on-site. This can speed up evaluations. Examples of apps with similar features include Mobile MIM.
- Booking and health scheduling: Telehealth apps can also include scheduling apps and software. Clients can book time slots depending on availability. Examples include SimplyBook.me, Find out more about Doctor’s Appointment App Development.
Benefits associated with doctor on-demand apps
Telemedicine apps provide the following benefits to patients:
- 24-hour access to physicians;
- Reduced costs by eliminating unnecessary ER or doctor office visits;
- Maximum convenience – access to physicians from home, during work breaks, or when traveling;
- Easy access to a broader network of medical specialists without geographic restrictions;
- Ability to use health insurance plans;
- More transparent pricing;
- Care from the safety of home without exposure to germs in a waiting room;
- Access to prescriptions on weekends and evenings when the doctor’s office is closed.
Service providers stand to gain the following benefits by engaging with telehealth apps:
- Improved supervision of chronic diseases and better outcomes;
- Better flexibility with asynchronous virtual care apps as doctors and patients don’t have to be available at the same time;
- Reduced outpatient load for general care cases — hospitals can therefore prioritize urgent care cases;
- Shorter wait times and improved client satisfaction;
- Reduction of overheads associated with in-person visits;
- Better revenues with more bookings and live appointments;
- Reduction of patient no-shows — patients book appointments during their free time.
Contact us now to discuss your Doctor On-Demand app development project!
How doctor on-demand app works
The app solutions connect patients to board-certified doctors 24 hours a day using their phone, tablet, or computer. They work with both patients and providers. Now, here are common steps that patients go through:
Step 1: Registration
The patient creates a free account on the web or from the mobile app. Their personal data is stored securely and used for future visits.
Step 2: Requesting a visit and choosing the doctor
The app may display a list of available doctors, showcasing their names, experiences, clinics, and even ratings. Selecting “video call” provides an estimated wait time, and patients may schedule an appointment several days in advance.
Step 3: Answering information about the visit
Doctors may require some preliminary information. Patients can answer a few questions and even upload images of the condition. Some apps can allow the collection of information from smart thermometers and health apps.
Step 4: Selecting a pharmacy of choice
Providers may need to send prescriptions or make recommendations for over-the-counter medications during or after the visit. Some apps may allow customers to set their preferred pharmacy.
Step 5: Confirmation of the video consultation
Patients may need to confirm the consultation and will receive a confirmation notification via email or text. They may be requested to enable Push notifications to get reminders when the doctor is available.
Step 6: Live video or voice call
The patient joins the call by clicking on the notification. Visits may have a timer, for instance, 10 minutes. The doctor reviews the patient information, asks questions, and prescribes medication.
Here are the steps for providers:
- Sign up – Providers sign up and provide information to set up their public profiles.
- Receive bookings and visits – Doctors attend to patients on-demand or schedule their visits.
- Earn – The app bills clients and deposits the earnings to the provider’s account per visit.
Monetization strategies for on-demand doctor apps
The most recommended monetization strategies to drive consistent revenues include:
- Commissions from the Visit fee – The platform can deduct a certain percentage from the fees paid by the patient during the visit.
- Subscription-based model – In a B2B approach, the service can sell its services to employers who, in turn, offer them to employees. For B2C, the service can require customers to subscribe at a monthly fee.
- Sponsored or boosted listings – Providers may pay a fee for prominent placement on search results and recommendations.
- Premium app features: The app can charge fees to users to access certain premium features, such as free counseling, follow-up appointments, or wellness checks.
- Sponsorships: On-demand doctor apps may seek partnerships with service providers in the health sector.
*Due to the sensitive nature of on-demand doctor apps, some monetization approaches may impact the user experience and result in privacy concerns, such as running unrelated display ads from third-party platforms.
Challenges while developing a doctor-on-demand app

Developers and clients should watch out for certain pitfalls when undertaking the development process of a doctor-on-demand app.
1. An app should be easy to use (UX)
Designers should give careful thought to the appearance and feel of medical apps providing health services. It’s important to offer an uncluttered interface. Designers should take into account color meanings. Popular colors in the medical world include green, white, pink, and blue. Using the app should be quite simple, following the main page layout with buttons that clearly state the app’s functions.
2. GDPR and HIPAA compliance
Doctor on-demand apps must adhere to strict security standards that enforce the protection of sensitive data. If the app targets EU customers, it must have GDPR compliance.
Telemedicine apps may need to conform to the following guidelines in the US:
- HIPAA
Telehealth platforms must comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA). One of its main precepts is to safeguard the patient’s personal and medical data.The HHS issues guidance on telehealth HIPAA matters and provides resources for mobile health app developers.
- DEA
The Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) provides federal oversight of controlled substances. Before the pandemic, it prohibited doctors from prescribing controlled substances without a prior personal visit or under certain special conditions.During the COVID public health crisis, the DEA removed the need for an in-person medical evaluation and allowed practitioners to prescribe buprenorphine following a telephone evaluation.
The DEA also requires apps used for filling or prescribing electronic prescriptions to undergo EPCS testing and certification, offered by testing labs such as UL Solutions in California.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS)
The CMS similarly published a Medicaid Tool kit with statutory and regulatory requirements in relation to telehealth. - Local guidelines
States have adopted their own policies governing the provision of telehealth services.Other regulations and guidelines that may be applicable include:- FDA Mobile Medical Applications Guidance
- The access rights, health apps, & APIs – Office for Civil Rights
- HITECH Act
*So, it’s paramount to work with an experienced team during the doctor on-demand mobile app development to build a HIPAA-compliant platform.
3. Video & audio streaming architecture
Doctor on Demand apps primarily rely on audio or video calls for communication. The video has to be live streamed from the user’s device to the provider and back.
Critical aspects of the architecture include the video streaming protocol (encoder & playback) and video server that temporarily stores and relays the video to the end-user.
It will be paramount to choose flexible, reliable, and scalable streaming engine providers such as Wowza and Flashphoner to provide the underlying streaming technology.
4. Scaling and performance
The app must be carefully designed to prevent common performance issues that can cripple the user experience, for instance, slow loading time, traffic spikes, DNS issues, etc. For proper design, it may be necessary to have DevOps on the team to design and configure the app infrastructure.
Main features for doctor on-demand app
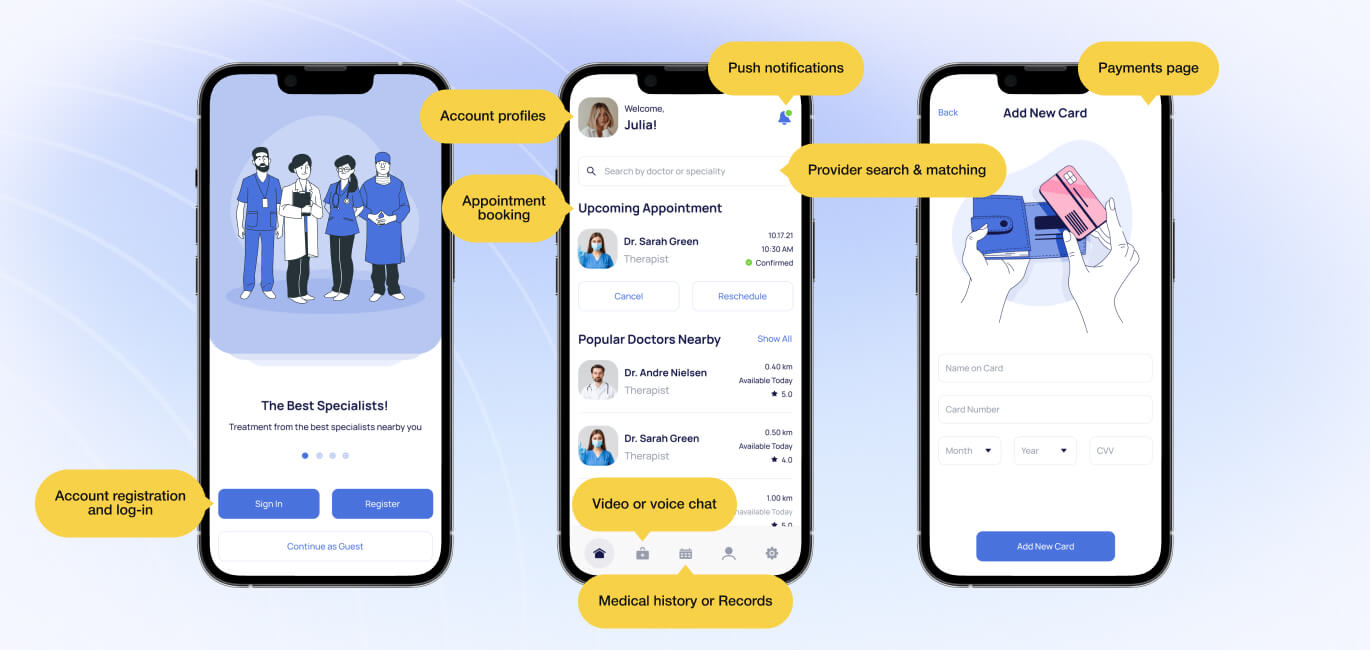
When figuring out how to make a doctor on-demand app, it’s essential to know the main features for patients and doctors.
Patients (app)
- Account registration and log-in: Multi-factor authentication is recommended for enhanced security.
- Push notifications: For alerts and reminders of upcoming meetings.
- Account profiles: Individual accounts or multiple account profiles for family members sharing the same account.
- Appointment booking: For scheduling video calls at an appropriate time.
- Payments page: To make payments for services without insurance using credit cards or with HSA, FSA, or HRA cards for eligible plans.
- Provider search & matching: To find providers using search criteria (specialty, gender, language, etc.) or receive recommendations after answering a few questions.
- Pharmacy selection: The doctor will need it to prescribe medication.
- Text notifications: Patients can leave their phone number to receive text notifications (optional).
- Medical history or Records: Patients can provide a brief medical history before interacting with the app and update it yearly.
- Video or voice chat: Both voice and video interactions may be permitted *, but certain medication prescriptions may be restricted from phone voice visits.
Doctors (app/web)
- Account registration and login: Maybe secure with two-factor authentication.
- Patient visits summary: Summary of the patient’s visit: conditions, prescribed medications, duration, and other details.
- Health questionnaire: To screen patients and their symptoms before the live call.
- Apple Health integration: To collect vital information: patient’s blood temperate, blood pressure, and heart rate.
- E-prescription: To prescribe medications and send prescriptions to an appropriate pharmacy based on the user’s selection or geolocation.
- Virtual waiting room: Breakdown of upcoming appointments with the ability to cancel or reschedule;
- Patient summary: May include patient information, health summary, and last visit information.
- Providers panel: Virtual dashboard offering access to different account sections, such as messaging, settings, payments history, etc.
Required tech stack for doctor on-demand app
The following technologies may be relevant when developing doctor on-demand apps:
- Video streaming APIs: The technologies facilitate real-time video communications on browsers and mobile apps, providing functions such as stream encoding, stream ingestion, storage, and playback. The streaming media server platform should be scalable and flexible to support popular streaming protocols. Examples include Flashphone, Wowza, and Twilio.
- CDN: A Content Delivery Network (CDN) speeds up the delivery of video content to user devices, reducing lagging and other issues. Top providers include Amazon CloudFront, Akamai, and Azure CDN.
- Technology platforms: Apps may be developed for the following computing platforms:
- iOS – with Objective-C or Swift
- Android – with Java or Kotlin
- Web (browser-based) – with Javascript, Express.js, Html5
- Cross-platform (one-code base multiple platforms) – via Flutter
- Backend: The backend stores and manipulates the app’s logic. Languages used for backend development may include Python, Django, Ruby, or Node.js.
- Payment processing: Doctor on-demand apps use payment APIs to accept customer payments. Top APIs include Braintree SDK, PayPal API, & Stripe API.
- Database: Database management platforms that can be used to build highly secure apps include Cassandra, HBase, MongoDB, & Postgres.
- Location data: Medical apps may need to display the user’s position on the map. Map SDKs include the AppKit framework for iOS and Google Maps SDK for Android.
- Healthcare & third-party security APIs: The demand for data, security, e-prescription, and insurance payment features necessitates developers to use other third-party APIs. Some implementations include TrueVault API (data privacy compliance), Vericred (health insurance data), Getsafe (health care insurance support), and Human API (health data).
Required team structure for doctor on-demand app development
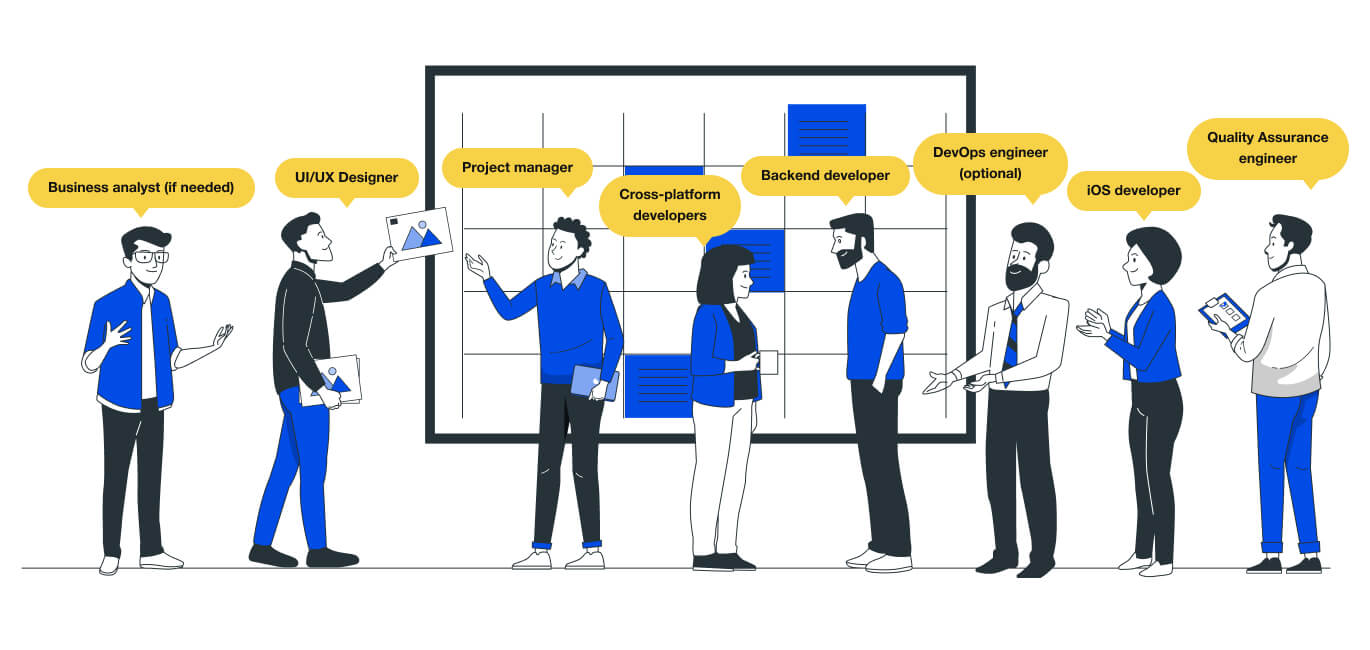
What is the ideal team composition for doctor on-demand app development? It’s helpful to have the following experts on board:
- Business analyst (if needed) – Validates requirements, plans development activities and evaluates ideas.;
- Project manager – Plans and schedules activities, prepares the budget and ensures proper execution & delivery of the project;
- UI/UX Designer – Evaluate user requirements, illustrates design ideas, and designs GUI elements;
- Backend developer – Creates, tests, debugs and maintains the app’s backend including the core logic and database;
- iOS developer – Builds applications for iOS devices using Swift or Java;
- Android developer – Codes apps for Android, using platform-specific languages;
- Cross-platform developers – Uses a cross-platform technology such as Flutter to build apps targeting multiple platforms using one code base;
- Quality Assurance engineer – Performs functional testing, identifies problems and discusses appropriate fixes;
- DevOps engineer (optional) – Handles app infrastructure, streamlines development with automation, and ensures the development of secure code.
When working with an app development company, the team selection should be made considering the project scope, complexity, schedule, and management approaches.
Steps to make a doctor-on-demand app
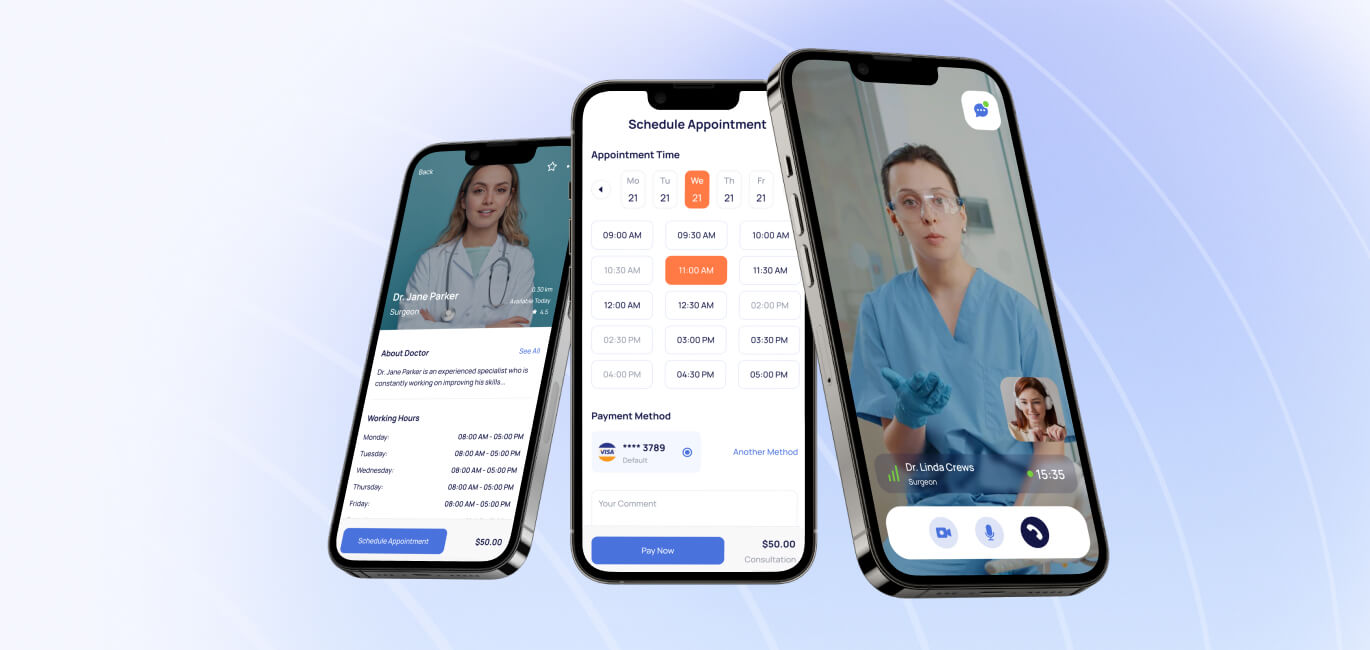
If you’re figuring out how to build a doctor-on-demand app, the following steps can help:
- Form a clear vision of your doctor-app idea
The idea should be solid and properly formulated. Start by analyzing the market demand and look for a strong market fit. It’s important to evaluate both direct and indirect competitors, paying attention to the strongest rivals and looking for gaps in their services —from negative user ratings. Medical services are quite sensitive, so it’s invaluable to know the people who are most likely to use the service. - Find developers
The development process is quite intricate, and it’s crucial to hire a team with relevant development experience even when developing for other markets. The company should comply with HIPAA, PCI, GDPR, and other security standards.One of the best places to find developers from offshore markets is on Clutch. It does a wonderful job of displaying verified reviews with a good selection of companies to choose from. Other places to find teams include GoodFirms and The Manifest. - Prototypes and design
The prototyping stage allows the design team to experiment and elaborate on the visual look of the app. It may entail coming up with user stories, drawing storyboards, sketching, and building a low-fidelity prototype —with limited interactivity.Once the prototype is validated, the team can build a high-fidelity prototype. The stage ends with developer hand-off, allowing the programmers to start implementing the design in code. - Build an MVP
The minimum viable product (MVP) contains the minimum amount of features for the day one launch. It’s a useful app that can help test the viability of the project. Here’s a comparison of must-have features to focus on during the demand doctor app development:Features for patients Features for providers Super admin features Sign up/Log-in for patients Sign-up/Sign up/Log-in for practitioners Secure login Patient profile for updating info, uploading doc & adding billing Provider’s panel to update info, view earnings, patients, etc. Records management Search feature to find doctors with filters for different specialties Health questionnaire for patient intake, with the ability to upload photos Search feature to view registered practitioners Appointment and prescription history Electronic medical record documentation tool and e-prescription Number of appointments tracking & appointment management Push or email notifications for upcoming visits Waiting room to view and manage appointments Resource health alerts *We recommend building the MVP with a Flutter app development service.
- Release and improve
The developer releases the MVP by publishing it on the appropriate app store or making the online version available. This is only the beginning. It’s important to keep collecting user engagement metrics and analyzing them to know which changes to make or advanced features to add.
Cost to develop a doctor-on-demand app
What influences the cost to create a doctor-on-demand mobile app? The costs typically boil down to the amount of time spent on the development process, from start to finish. Factors that can affect the development time include:
- Design complexity: It’s influenced by the number of screens, User interface sophistication, and the number of custom elements.
- Number of complex features: The app’s complexity will influence the time spent working on the core logic, backend, and third-party integrations.
- Development option (native apps or cross-platform): It takes more time to develop native apps for iOS and Android. Cross-platform development saves time with code reusability, reducing the doctor on-demand app development cost.
- Team composition: A highly-specialized team with many experts may be more expensive to maintain compared to a simple team. Choosing the right region such as Eastern Europe can allow clients to stretch their budgets and have all the expertise required.
When providing an estimate, the company may try to calculate the overall development time and multiply the total with their hourly rate. Given the intricacies of developing doctor-on-demand apps, it may take 1,000+ hours.
So, how much does it cost to make a doctor on-demand app? The minimum cost of developing an MVP may start from $52,000 in Eastern Europe and more than $100,000 in the US.
And how long will it take? According to our experience, it may take 4 to 6 months.
Conclusion
Covid-19 significantly changed the way consumers think about healthcare, with more people now open to using telehealth applications for doctor visits. As of July 2021,
McKinsey noted that utilization had stabilized at levels 38 times higher than pre-pandemic levels.
Current solutions are not nearly perfect, opening doors for new entrants into the space. Most of the progress has been in the US, meaning that many other markets are ripe for opportunity.
Given the intricacies of doctor app development, it’s paramount to choose a distinguished app development company. Attractgroup has this requisite experience, having been involved in telehealth and mental health projects:
- Bausey Urgent Care: Web app built to facilitate urgent medical care needs of schools in New Orleans, with super admin, nurse, and doctor roles.
- Blue Moon: An iOS and Android app developed to connect mental health practitioners with senior patients for in-home counseling).
- Clinisoft: A CRM/HRM/ERP system targeted at a chain of clinics.
- Sleeptrack: Sleep monitoring Flutter App for the mental health space (Learn How to Develop a Mental Health App)
digital marketing for doctor on demand, doctor app builder, doctor on demand clone, doctor on demand, digital marketing agency, doctor on demand digital marketing company, digital marketing, digital marketing strategies, social media marketing, search engine optimization, digital marketing tools










